Pesticides and the climate crisis
Food systems account for over one-third of Global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, which includes agriculture and pesticide use. Pesticides exacerbate the climate emergency throughout their lifecycle via manufacturing, packaging, transportation, application, and through environmental and soil degradation. Many of the world’s biggest oil companies such as ExxonMobil, Shell and ChevronPhillips Chemical produce pesticides or their chemical ingredients.
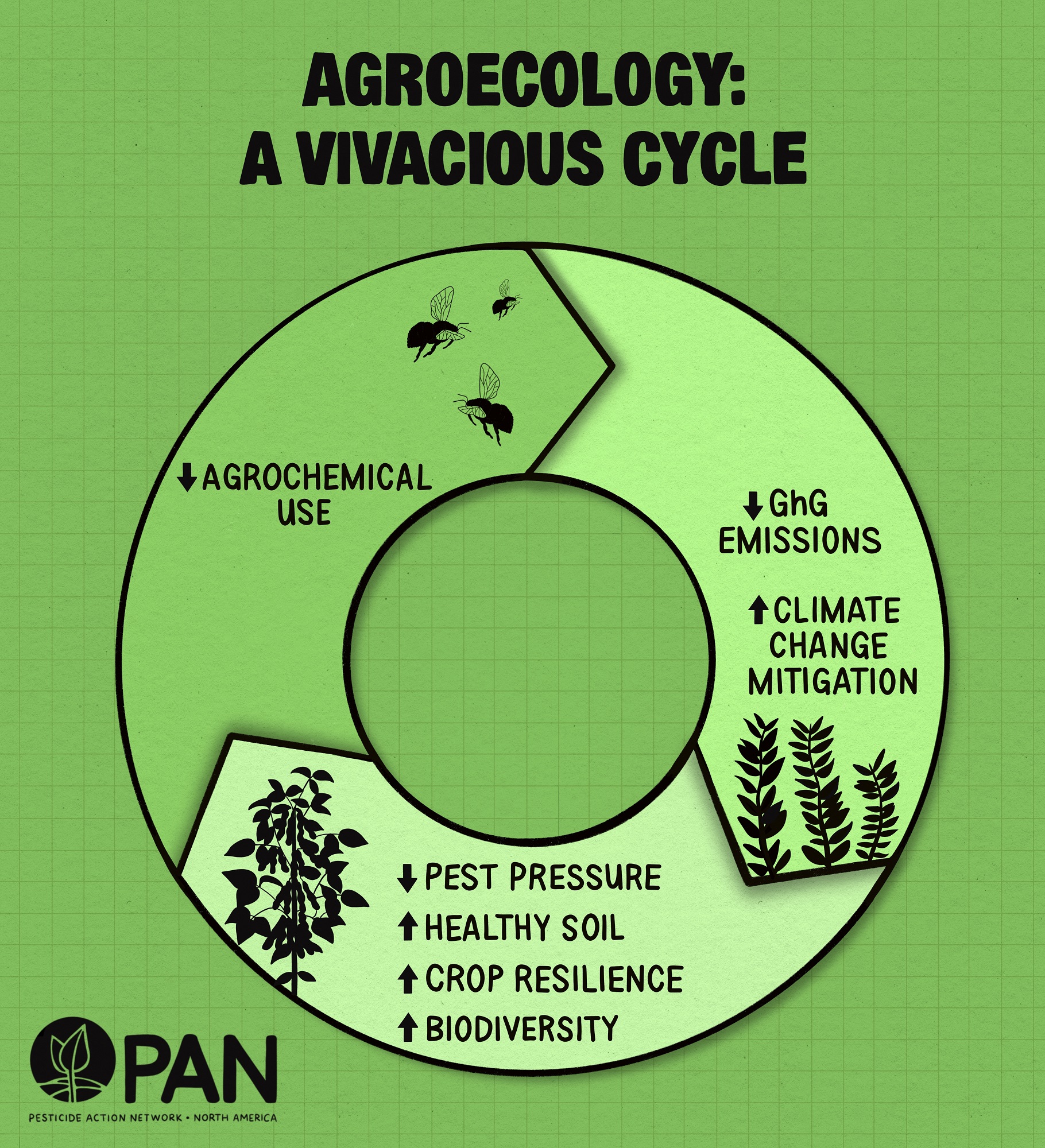
The impacts of the climate emergency are expected to lead to an increase in pesticide use, which will create a vicious cycle between chemical dependency and worsening climate breakdown. As temperatures rise, the number of pests increase and crop resilience goes down, requiring ever-larger amounts of pesticides. This rise in pesticide use will cause insects and weeds to develop resistance to herbicides and insecticides in greater numbers, while also continuing to harm human health and the environment.
Despite this, pesticide reduction as a climate solution has largely been ignored. Pesticide use is even presented as a climate mitigation strategy by the agro-chemical industry, which perpetuates the myth that intensifying food production through the continuous use of harmful chemicals is the only way to guarantee global food security while protecting precious habitats.
Farming systems that reduce reliance on pesticides, including agroecology, are a clear solution. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reports that agroecological farming could cut emissions by the equivalent of 10% of global energy related CO2e emissions. PAN UK is working to promote pesticide reforms and the increased uptake of agroecology as it is important to national climate action globally.
Cultivating coherent climate action – a briefing
In 2023, most Parties to the UN Framework Convention of Climate Change (UNFCCC) committed to integrate action on agriculture and food systems into their climate mitigation and adaptation plans by late 2025. The briefing Cultivating Coherent Climate Action highlights how nearly all of these countries have already committed to relevant agriculture-sector reforms in other related UN policy instruments, including:
- the phase out of Highly Hazardous Pesticides (HHPs) in agriculture
- an at least half reduction in risk from pesticides and,
- commitments to substantially increase support for agroecological farming systems.
Integrating these commitments into national climate plans will help countries deliver key global commitments on agriculture and food systems across the three UN policy frameworks to address the triple planetary crisis of climate change, biodiversity loss, and pollution, while reducing the national burden of delivery.
A vicious cycle
The UK government must take action to transform agriculture in order to avoid the worst effects of today’s climate and nature crises. Governmental policies addressing climate change should, therefore, include a focus on pesticide reduction as a key strategy for tackling greenhouse gas emissions and improving the climate resilience of food and farming system. Policies should be based on an approach underpinned by the growing body of evidence showing that pesticide use is both a direct and indirect driver of climate change, and not part of the solution.